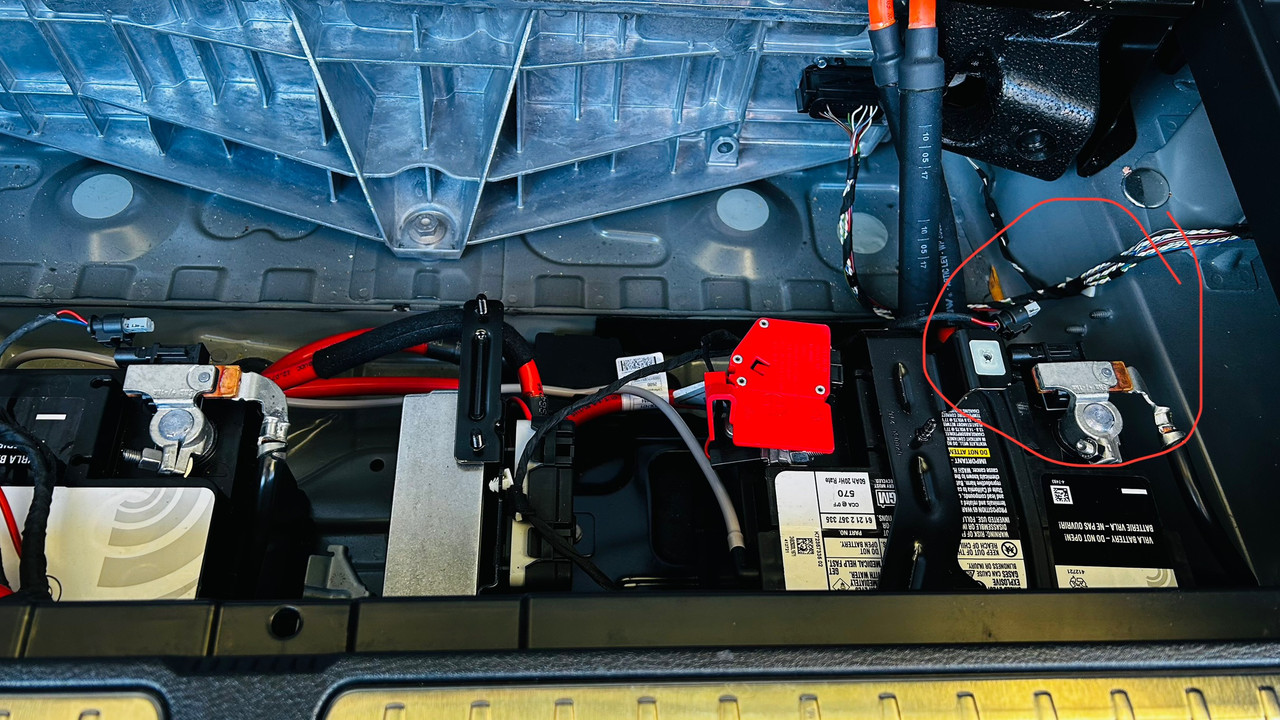
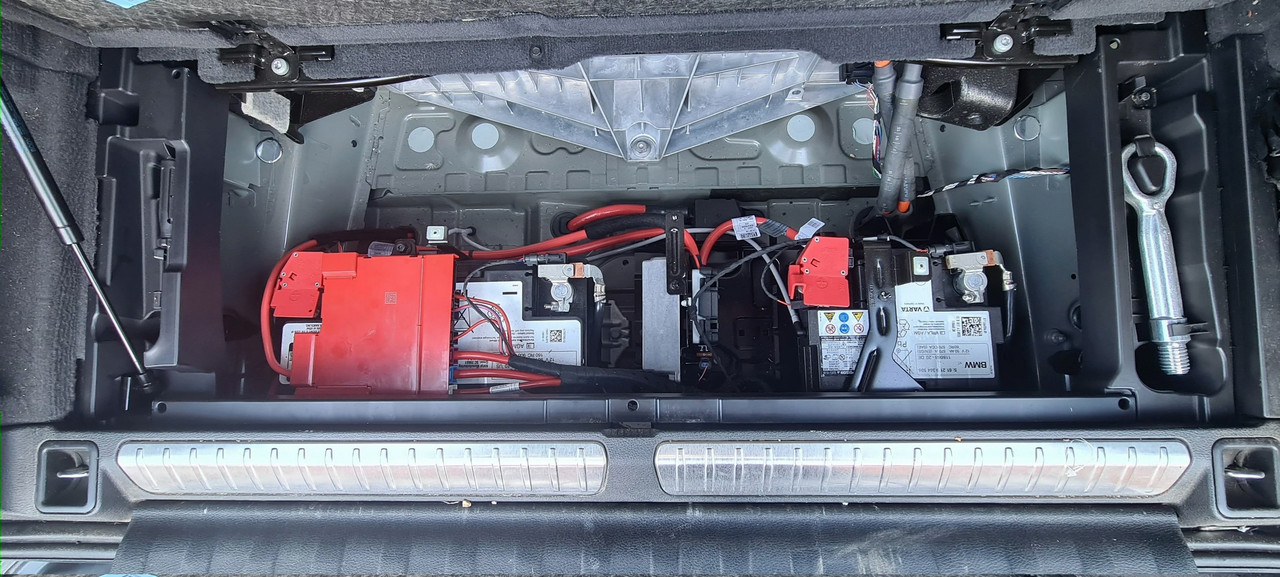
不好意思又来问你。你给的那个 realoem.com 很管用,不过我有个疑问。
你说的“The part number from BMW should be 61216819309.” 这个也是我ebay order 的part number。
不过realoem 上的图,那个小电池的negative cable 是没有IBS 的,而且part number 是 09. 61129255047
https://www.realoem.com/bmw/enUS/showpa ... 1216819309
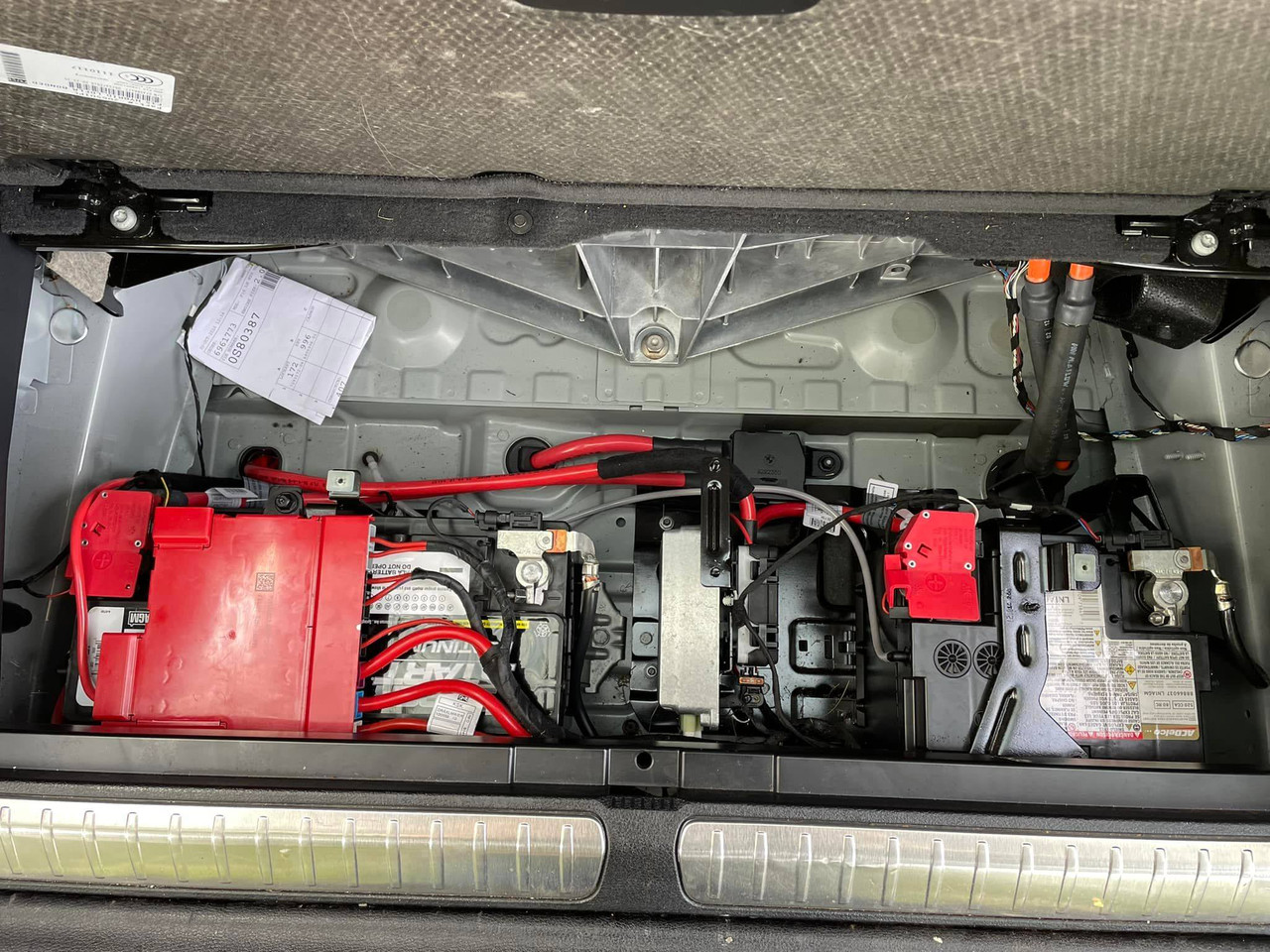
我的车,大小电池都是有ibs 的,好奇怪。
我现在是大电池插着IBS,小电池没插。
seymour 写了: 2025年 11月 16日 20:25A description of the IBS. note the section on startability limits. This is BMW copyrighted information. I may delete the reply in a couple of days.
The part number from BMW should be 61216819309.IBS: Intelligent battery sensor
The IBS is a mechatronic, intelligent battery sensor with its own microcontroller. The microcontroller is an element of the electronics module. The electronics module records the voltage, the current flow and the temperature of the battery. The following components are fitted in the electronics module:a measuring resistor for current measurement
a temperature sensor
evaluation electronics on a printed circuit boardIndex Explanation
1 Negative battery terminal
2 Intelligent battery sensor (IBS)
3 Battery earth lead
The IBS continuously measures the following values on the battery:Terminal voltage
Charge current
Discharge current
Battery temperature
For data transfer, the IBS is connected via a LIN bus (LIN stands for Local Interconnect Network) e.g. with the following control unit:Digital Motor Electronics (DME) or Digital Diesel Electronics (DDE) or Electrical Digital Motor Electronics (EDME)
Index Explanation Index Explanation
1 Measurement of the battery voltage between the positive battery terminal and negative battery terminal 2 Temperature measurement of the battery (T)
3 Microcontroller (μC) in the intelligent battery sensor (IBS) 4 Digital Motor Electronics (DME) or Digital Diesel Electronics (DDE) or Electrical Digital Motor Electronics (EDME)
5 Measuring resistor (current measurement (A) via voltage drop (V) at measuring resistor) 6 Negative battery terminal
7 Positive battery terminal
LIN bus LIN bus for transmission of the values to the DME or DDE or EDME
System functions
The following system function of the power management with IBS ("Advanced Power Management") is described:
Determining state of charge
Determining the startability limit
Determining the battery condition
State of charge
The APM (Advanced Power Management) with the intelligent battery sensor (IBS) determines the state of charge while driving and when the vehicle is at a standstill with the help of measured data:Driving:
Balancing the charge and discharge current of the battery.
Calculation of the current characteristics on engine start to ascertain the battery condition.
While driving, the IBS transfers the data across the LIN bus bit to the engine control unit (DME, DDE, EDME). The software in the IBS controls the communication with the higher-level engine control unit (DME, DDE, EDME).Vehicle standstill
When the vehicle is at a standstill, the measured values (open-circuit voltage measurement) are queried in cycles to detect energy losses. The measured values are entered in the IBS in the memory and transferred to the DME, DDE or EDME after restarting the engine.
For the history of the state of charge, the following values are stored in the DME, DDE, EDME:
Battery state of charge of the last 5 days.
Charge status histogram showing periods in the ranges 0 - 20 %, 20 - 40 %, 40 - 60 %, 60 - 80 % and 80 - 100 %. The charge status histogram is reset in the following cases: programming the DME, DDE or EDME or registering a battery exchange.Note!
Evaluating state of charge
The battery voltage measured by the IBS approaches the actual open-circuit voltage slowly after the vehicle has gone to sleep. The accuracy of the measured value increases with the duration of the rest phase: The measured state of charge is reliable after a rest phase of at least 3 hours. However, an insufficient rest phase or standby current violation may result in the state of charge not being properly determined: the state of charge is implausible.
Startability limit
The APM calculates a lower and an upper startability limit for the battery:The lower startability limit corresponds to the minimum charge state of the battery so that the vehicle can still be started.
To counteract discharge down to the bottom startability limit, a certain charge volume is kept as a reserve. To achieve this, the upper startability limit is calculated. This value is used e.g. as the limit value for the requests for deactivation of terminal 30B when auxiliary consumers are active.
The startability limit is calculated by evaluating the following measured variables:Average ambient temperature with vehicle parked.
Ambient temperature of the last journey.
Current state of charge.
Voltage dip of the last engine start (trend for ageing of the battery).
The startability limit is therefore dependent on the ambient temperature: The colder the ambient temperature, the more energy required for the engine start. Therefore the startability limit is higher for cold ambient temperatures:Startability limit is approx. 30% state of charge at 15 °C.
Startability limit is approx. 50% state of charge at -15 °C.